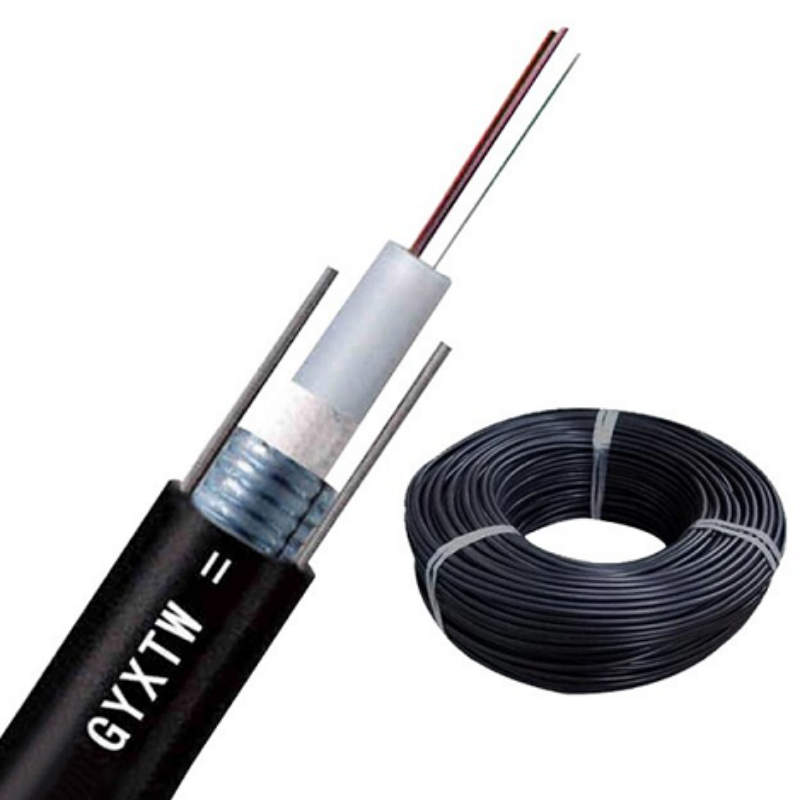
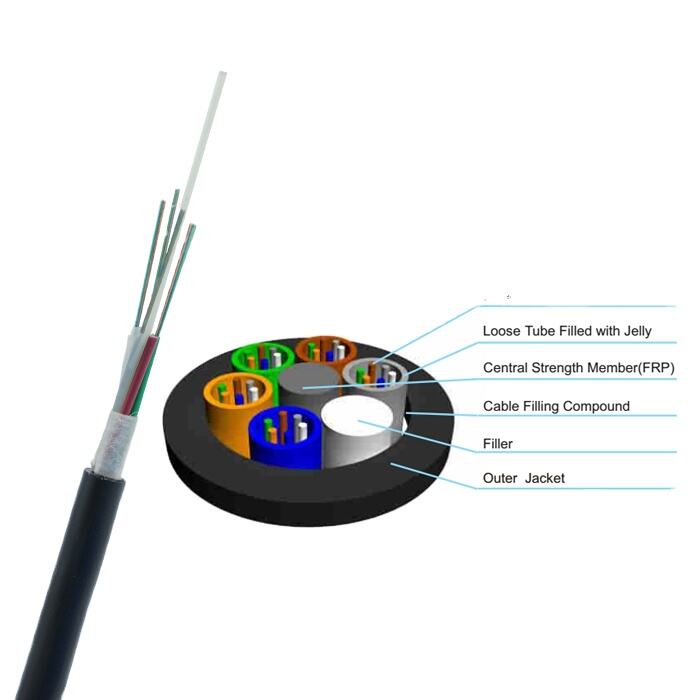
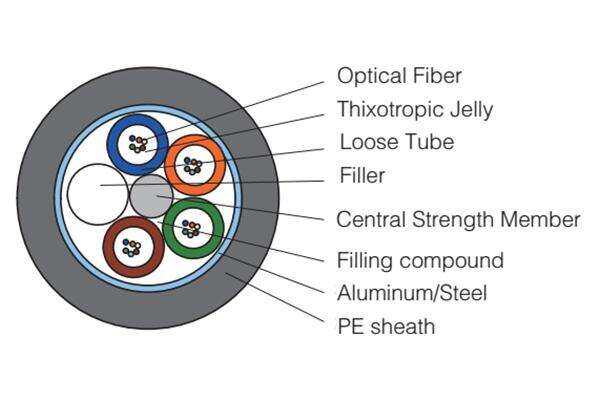
single mode fiber
Single mode fiber represents a cutting-edge optical fiber technology designed for long-distance data transmission. This specialized fiber features a small core diameter, typically 8-10 micrometers, which allows only one light mode to propagate through the fiber core. The fiber's construction consists of a central glass core surrounded by a cladding layer with a lower refractive index, enabling the transmission of light signals through the principle of total internal reflection. Operating primarily in the 1310nm and 1550nm wavelength windows, single mode fiber delivers exceptional bandwidth capacity and minimal signal distortion over extended distances. Its design effectively eliminates modal dispersion, a common issue in multimode fibers, resulting in superior signal integrity and reduced signal attenuation. The fiber's ability to maintain signal quality over long distances makes it ideal for telecommunications infrastructure, internet backbone networks, and high-speed data centers. Additionally, single mode fiber supports advanced transmission technologies such as DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing), enabling multiple channels of data to be transmitted simultaneously on different wavelengths.