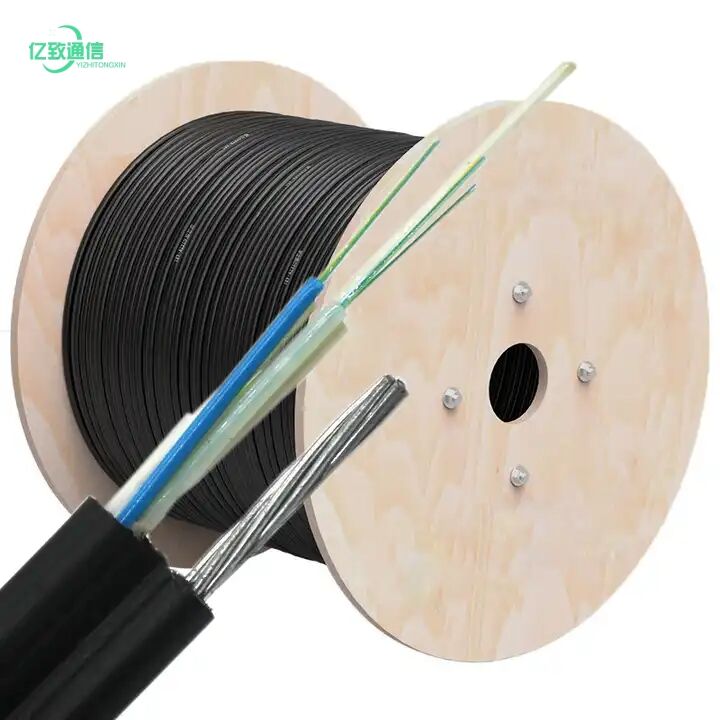
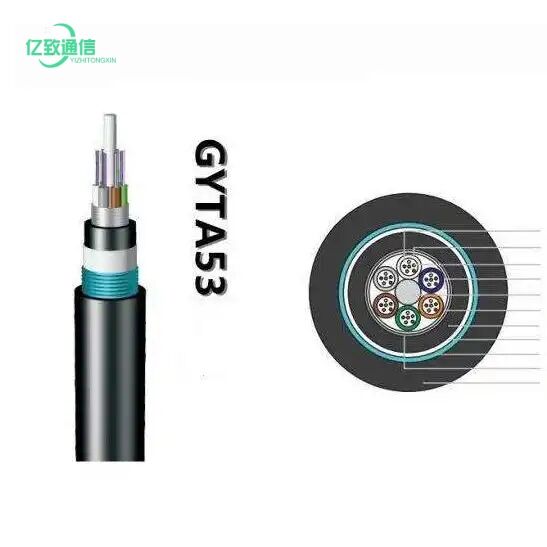
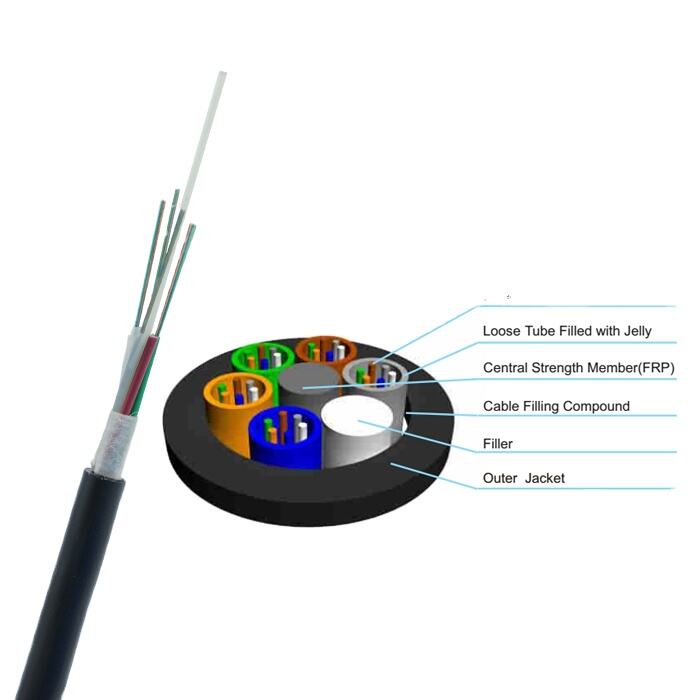
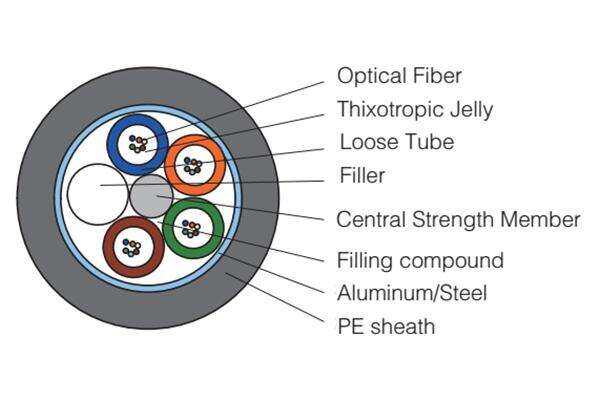
underground fiber cable
Underground fiber cable represents a cornerstone of modern telecommunications infrastructure, serving as the backbone of high-speed internet and data transmission networks. These cables consist of ultra-thin glass or plastic fibers that transmit information through pulses of light, offering unprecedented bandwidth capacity and speed. The installation process involves burying these cables at specific depths beneath the ground, protected by multiple layers of insulation and reinforcement materials. These cables are designed to withstand various environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations, moisture, and ground movement. The core technology employs total internal reflection, allowing light signals to travel long distances with minimal loss of signal strength. Modern underground fiber cables often incorporate advanced features such as fiber Bragg gratings for strain monitoring, specialized coating for enhanced durability, and redundant pathways for network reliability. Their applications span across telecommunications, internet service provision, corporate networks, military communications, and smart city infrastructure. The strategic placement underground provides natural protection from weather elements, vandalism, and accidental damage, while also maintaining aesthetic appeal in urban environments.