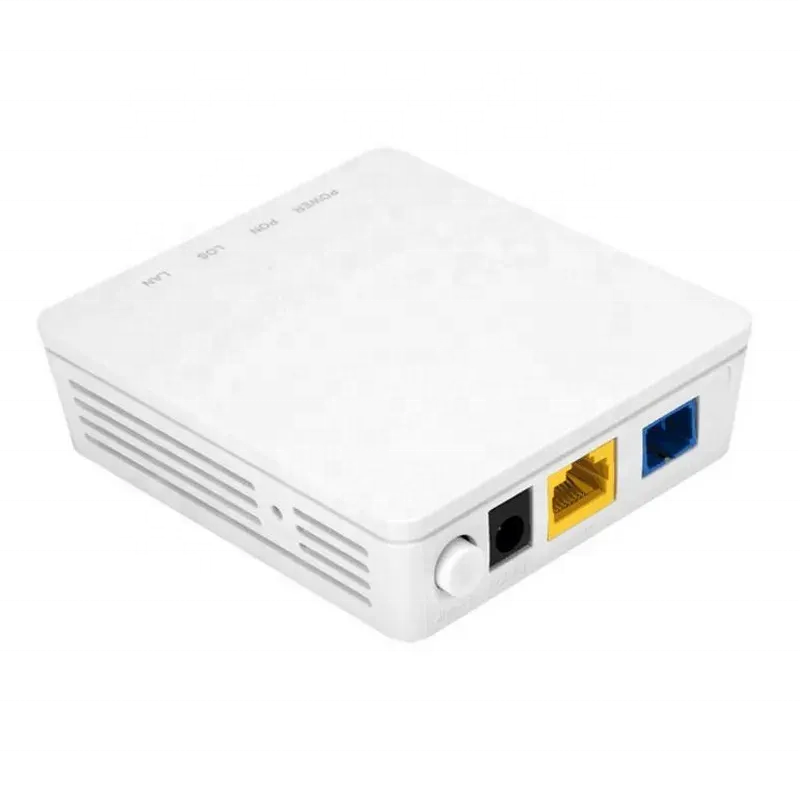
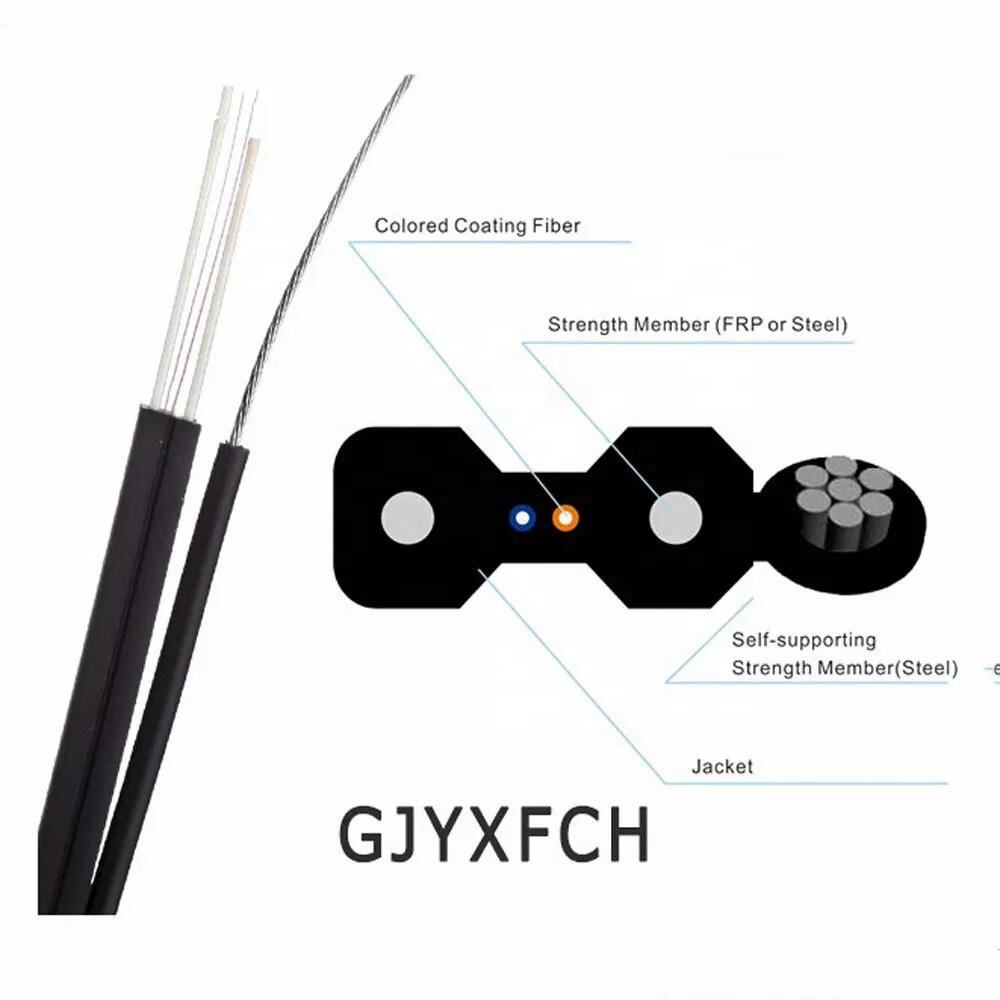
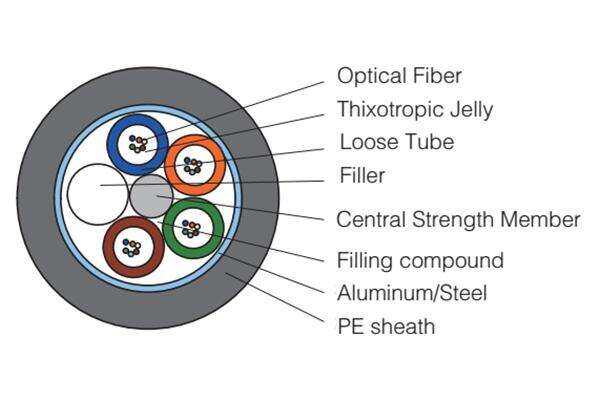
fiber optic single mode
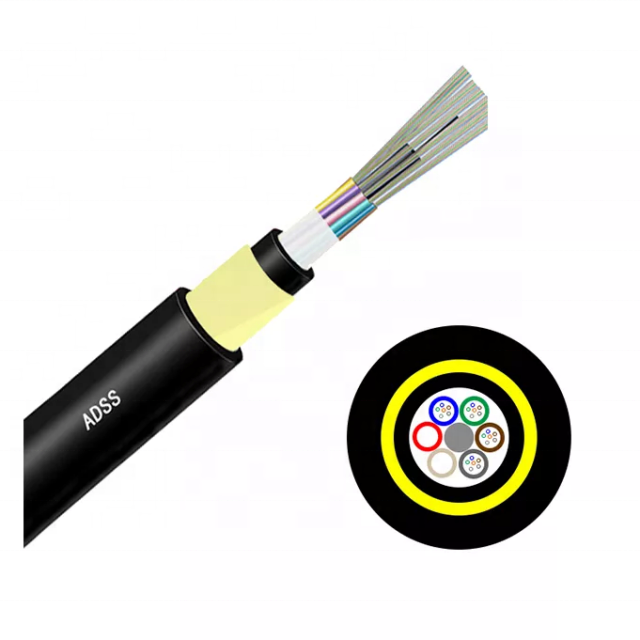
Fiber optic single mode cables represent the pinnacle of optical communication technology, designed to transmit a single ray of light through an incredibly thin glass core typically measuring 8 to 10 microns in diameter. This specialized design allows for the propagation of light in a straight path with minimal signal degradation, enabling data transmission over significantly longer distances compared to multimode fibers. The cable's core is surrounded by a cladding layer with a lower refractive index, ensuring that light signals remain confined within the core through total internal reflection. Single mode fibers operate at higher bandwidths and frequencies, typically using laser light sources in the 1310nm or 1550nm wavelength ranges. These characteristics make them ideal for long-distance communication networks, including telecommunications backbones, cable television distribution, and high-speed internet infrastructure. The technology's ability to maintain signal integrity over extended distances, combined with its superior bandwidth capabilities, has made it the preferred choice for critical telecommunications infrastructure and enterprise networks requiring reliable, high-speed data transmission. Single mode fibers are particularly valuable in metropolitan area networks, long-haul communications, and submarine cable systems, where data needs to travel over extensive distances without signal regeneration.