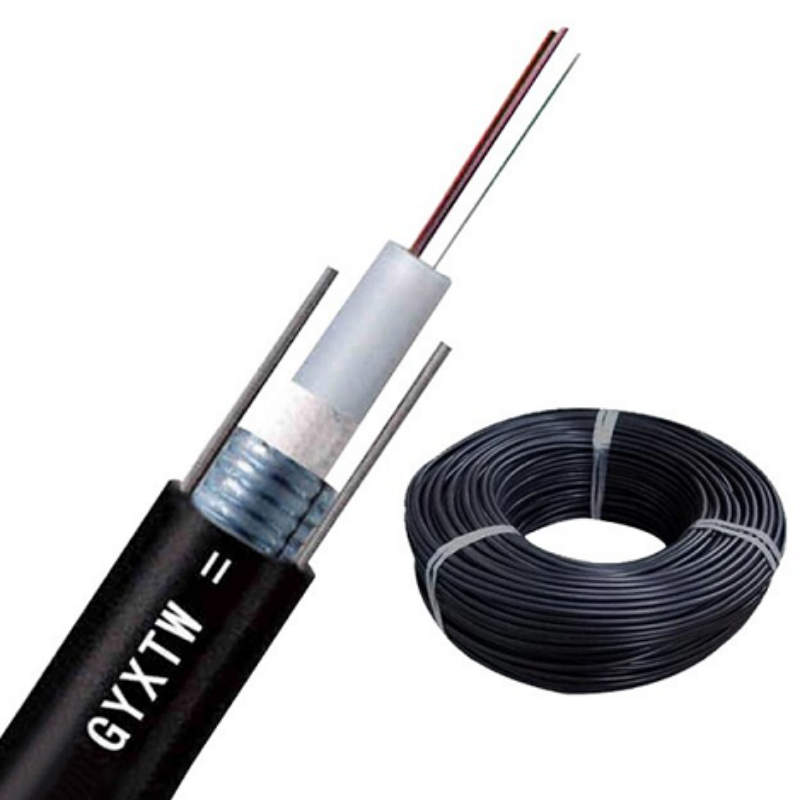
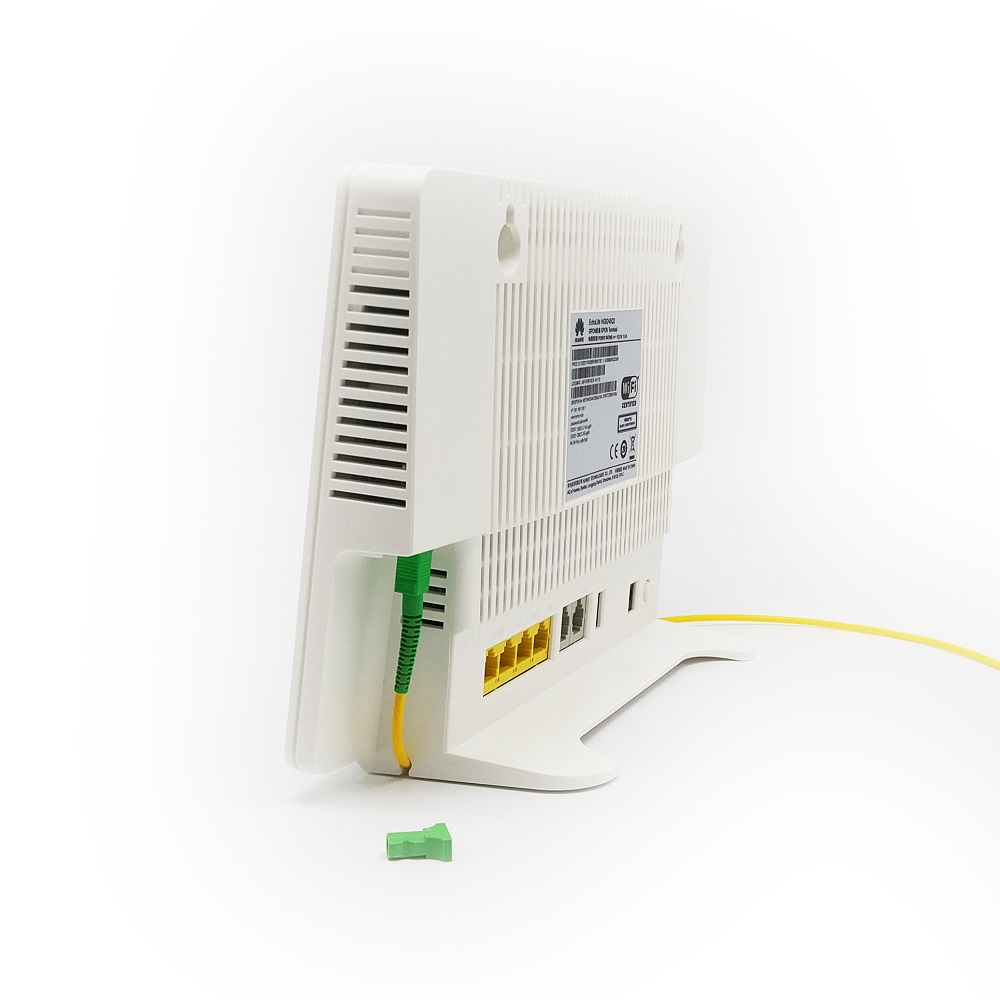
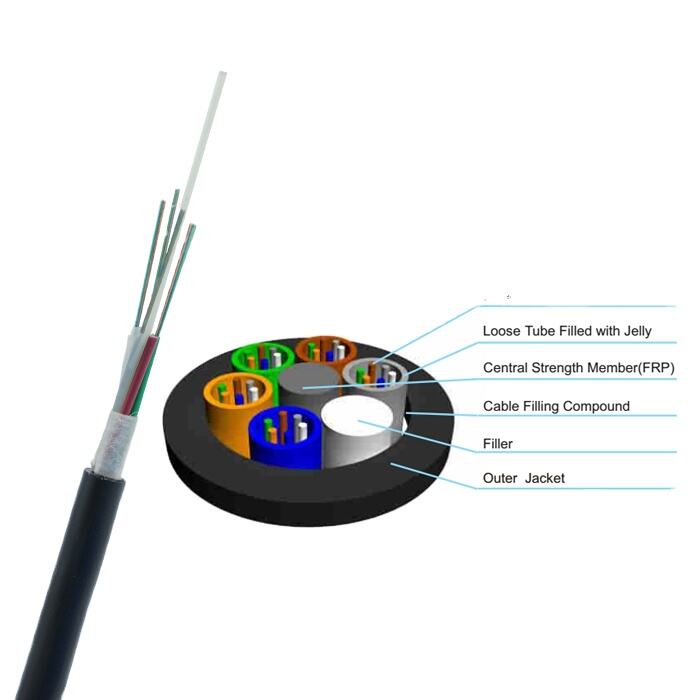
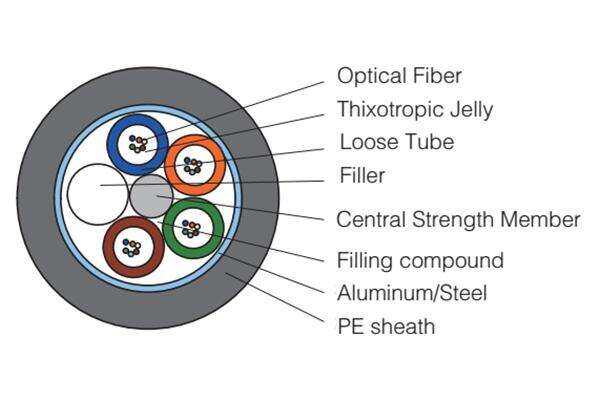
fiber cable
Fiber cable represents a groundbreaking advancement in telecommunications infrastructure, utilizing thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data through pulses of light. These cables consist of a core surrounded by a cladding layer and protective outer jacket, enabling the transmission of digital signals over long distances with minimal signal loss. The technology operates on the principle of total internal reflection, where light signals bounce along the core without escaping, maintaining data integrity throughout the transmission. Modern fiber cables can carry massive amounts of data at speeds approaching the speed of light, making them essential for high-speed internet connections, telecommunications networks, and data center operations. The cables come in various types, including single-mode for long-distance transmission and multi-mode for shorter distances, each optimized for specific applications. Their durability and resistance to electromagnetic interference make them ideal for both underground and overhead installations, while their small diameter and lightweight nature facilitate easy installation and maintenance. The technology continues to evolve with improvements in manufacturing processes, leading to enhanced performance characteristics and expanded applications across various industries.