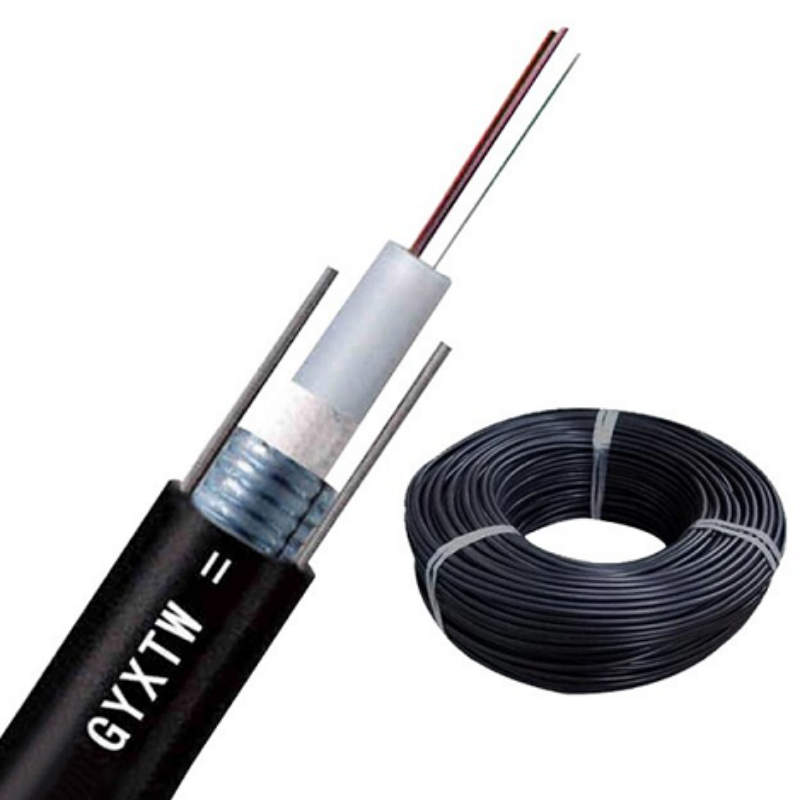
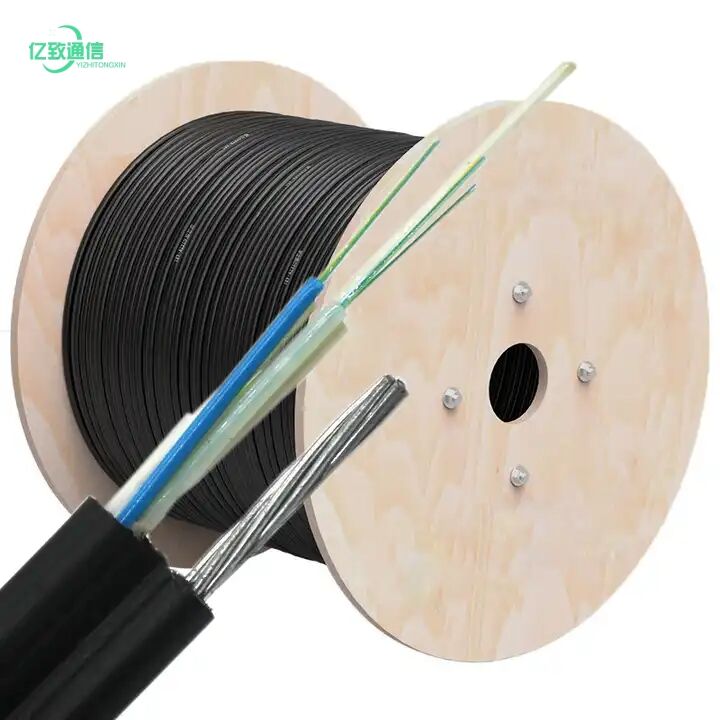
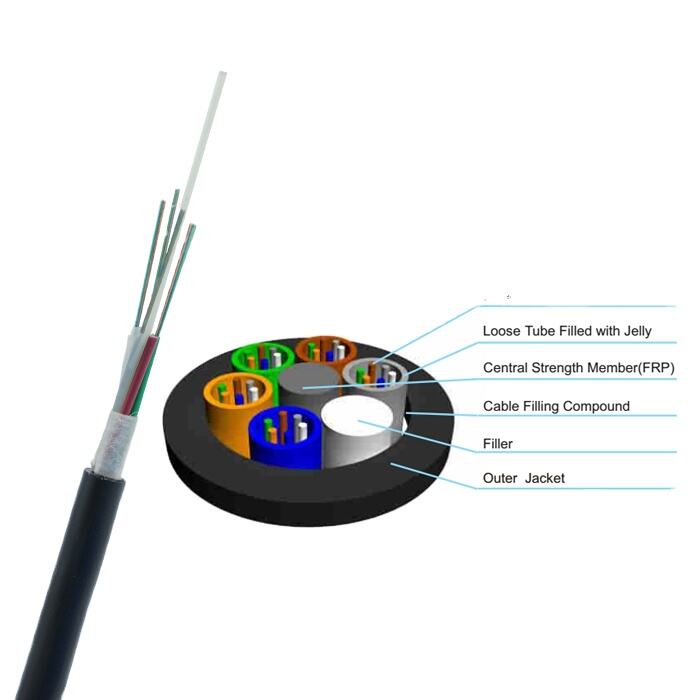
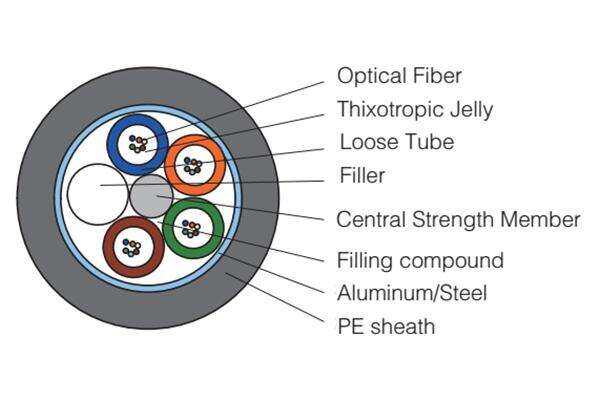
fiber optical cable
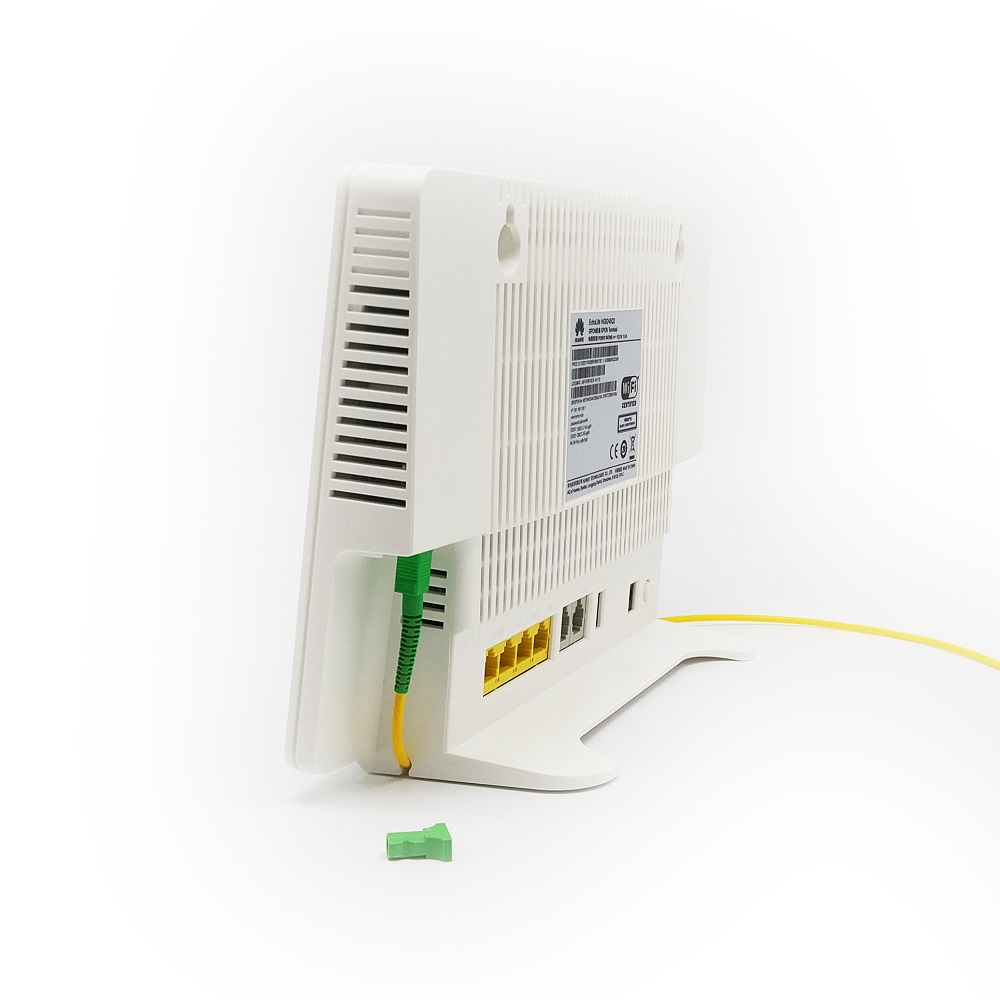
Fiber optical cable represents a groundbreaking advancement in telecommunications technology, utilizing thin strands of pure glass or plastic to transmit data through pulses of light. These cables consist of a core surrounded by a cladding layer and protective outer coating, enabling the transmission of digital information across vast distances at incredible speeds. The core, typically measuring just microns in diameter, carries light signals while the cladding reflects light back into the core, ensuring minimal signal loss. Operating on the principle of total internal reflection, fiber optical cables can transmit data over long distances without significant degradation, making them ideal for both short-range and long-haul communications. These cables support bandwidth capabilities far exceeding traditional copper cables, with modern systems capable of transmitting multiple terabits per second. Their implementation spans various sectors, from telecommunications and internet infrastructure to medical imaging and industrial automation. The technology's reliability in data transmission, combined with its resistance to electromagnetic interference, has made it the backbone of global communications networks, supporting everything from high-speed internet to international phone calls.